Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-09-24 Origin: Site











You will find several main types of lenses in endoscopes, including objective, relay, rod, GRIN, cylindrical, and aspheric lenses. Many endoscopes use lens sizes like 1/6", 1/10", and 1/18". The material and design of Endoscope Lenses affect both image clarity and how well you can see details during procedures. A well-designed lens can give you a wider field of view and less image distortion, which helps surgeons see more clearly and avoid mistakes.
Endoscope lenses come in various types, including objective, relay, rod, GRIN, cylindrical, and aspheric lenses, each serving a specific purpose in image clarity and detail.
Choosing the right lens material, such as optical glass or borosilicate glass, is crucial for durability and high-quality imaging during medical procedures.
Advanced lens designs, like precision lenses and metalens systems, enhance optical clarity and allow for real-time visual feedback, improving diagnostic accuracy.
Proper cleaning and sterilization of endoscope lenses are essential to maintain their performance and ensure patient safety during medical procedures.
Understanding the functions of different lens types helps medical professionals select the best endoscope for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
Endoscope lenses play a vital role in capturing and transmitting images inside the body. Each type of lens in an endoscope serves a specific function to ensure you get clear, accurate visuals during medical procedures. Here’s a breakdown of the main types of endoscope lenses and how they work together to deliver high-quality images.
Objective lenses sit at the very tip of the endoscope. You rely on these lenses to capture light from the area under examination and focus it onto the imaging system. The design of objective lenses directly affects the clarity and brightness of the images you see.
Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
Light Capture | Collects light from the target area and surroundings |
Image Clarity | Produces clear, bright images over a wide area |
Outer Diameter | Maintains a slim profile for minimally invasive procedures |
Biocompatibility | Safe for use in medical environments |
Lens Type | Can include SELFOC® (a gradient index lens with a cylindrical shape) |
Viewing Angle | Offers a wide field of view, up to 70 degrees |
Aberration | Designed for low aberration, improving image quality |
Size Availability | Available in extremely thin sizes, down to 0.2 mm in diameter |
You depend on objective lenses to form the initial image. They focus the view of tissues or organs onto the next part of the optical system. The focal point of the lens determines how much of the scene stays in focus, which is called the depth of field. In modern endoscope lenses, this depth can range from 3 to 100 mm, giving you flexibility for different procedures.
Relay lenses transmit the image from the objective lens down the length of the endoscope to your eyepiece or camera. These lenses keep the image sharp and undistorted, even as it travels through the long, narrow tube of the endoscope.
Function | Description |
|---|---|
Image Reception | Receives the image from the objective lens |
Image Transmission | Passes the image smoothly to the eyepiece or camera |
Light Path Manipulation | Adjusts the path of light through the endoscope |
System Length Extension | Extends the optical system to reach deeper areas |
Image Inversion | Can flip the image to maintain correct orientation |
Image Rectification | Adjusts the image as needed for accurate viewing |
Relay lenses are essential when you need to observe areas that are not easily accessible. They preserve image quality and allow you to see fine details, even at a distance from the target area.
Rod lenses are cylindrical and fit snugly inside the endoscope tube. You use these lenses to focus and direct light efficiently through the device.
Rod lenses are polished on the sides and ground flat on both ends.
They align themselves with the tube, providing both optical and structural support.
These lenses focus light into a line, which is useful for shaping and directing beams.
Feature | Rod Lenses | Other Lens Types |
|---|---|---|
Shape | Cylindrical | Various shapes |
Focusing Capability | Focuses light to a line | Varies |
Focal Length | Very short | Generally longer |
Optical Power | High | Varies |
Spherical Aberrations | Can be significant | Varies |
Rod lenses help you achieve a compact design for the endoscope while maintaining strong image transmission. They are especially valuable in medical instruments that require both durability and precision.
GRIN (Gradient Index) lenses have a refractive index that changes gradually from the center to the edge. This unique design lets you focus light precisely, even in very tight spaces.
The refractive index gradient allows the lens to bend and focus light onto a specific point.
GRIN lenses are ideal for imaging inside small or delicate areas, such as biological tissues.
You can use GRIN lenses in combination with miniature microscopes for detailed imaging.
GRIN lenses also support miniaturization. For example, a GRIN lens with a diameter of just 500 micrometers can bend without breaking and still maintain image quality. Even if the lens shifts slightly, it keeps the resolution and signal strong. This makes GRIN lenses perfect for endoscope lenses that need to be both small and reliable.
Cylindrical and aspheric lenses further enhance the performance of endoscope lenses. Each type brings unique benefits to medical imaging.
Aspherical lenses reduce spherical aberrations, which improves resolution and allows you to see tissues and organs more clearly.
Cylindrical lenses correct distortion along one axis, making images sharper and more accurate.
These lenses help you get clearer visuals of areas like the digestive tract, which supports better diagnosis.
Aspheric lenses have a variable curvature, which corrects multiple types of optical errors, such as coma and astigmatism.
By minimizing these aberrations, aspheric lenses give you sharper images and higher contrast.
You often find aspheric lenses paired with GRIN lenses in advanced endoscope lenses. This combination boosts optical performance, which is crucial for high-precision tasks, such as imaging deep brain regions or detecting subtle changes in tissue.
By understanding the roles of each lens type, you can appreciate how endoscope lenses work together to deliver the best possible images during medical procedures.
When you select an endoscope, you need to consider the lens materials. The right choice affects both durability and image quality. Here’s how the most common materials perform in endoscope lenses.
Optical glass remains a top choice for endoscope lens materials. You benefit from its excellent light transmittance and stable optical properties. This material gives you clear images, which is essential for accurate diagnosis.
Property | Description |
|---|---|
Refractive index | Helps achieve specific optical effects for sharp imaging |
Dispersion property | Low dispersion keeps images clear and accurate |
Thermal stability | Maintains performance across a wide temperature range |
Light transmittance | High transmittance ensures bright, clear visuals |
Chemical stability | Resists corrosion for long-term reliability |
Processing performance | Allows for precise manufacturing of various lens shapes |
You can rely on optical glass for consistent performance in most medical environments. Its durability supports repeated use, while its optical properties help maintain high image quality.
Borosilicate glass stands out for its resistance to thermal shock and chemical corrosion. You often see this material in endoscope lenses used in harsh or variable environments.
Property | Borosilicate Glass | Regular Glass |
|---|---|---|
Coefficient of Thermal Expansion | Very low | Higher |
Resistance to Thermal Shock | Highly resistant | Less resistant |
Maximum Temperature Endurance | Up to 500 °C (930 °F) | Lower |
Chemical Resistance | Highly resistant to acids and chemicals | Less resistant |
Stability in Corrosive Environments | Exceptional due to low alkali content | Lower stability |
You gain peace of mind knowing borosilicate glass can handle sudden temperature changes and exposure to chemicals. This stability helps preserve image quality during demanding procedures.
Fused silica offers unique advantages for endoscope lens materials. You get high light transmission across a wide spectrum, which improves image quality in both visible and ultraviolet ranges.
Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
Range of Transmission | Transmits over 90% of light from 200nm to 2 microns |
Low Coefficient of Expansion | Resists thermal shock, maintains surface accuracy |
Minimal/No Fluorescence | Reduces background noise in optical systems |
High Chemical Resistance | Remains inert in harsh environments |
Tip: Fused silica’s low fluorescence makes it ideal for advanced imaging, such as fluorescence endoscopy, where you need a high signal-to-noise ratio.
You can trust fused silica to deliver reliable performance and excellent image quality, even in challenging medical settings.
You rely on specialized lenses in fluorescence endoscopy to detect and visualize fluorescent signals inside the body. These lenses help you see tissues that absorb fluorescent dyes and emit light at specific wavelengths. You need precise illumination at the excitation wavelength to activate these dyes. The endoscope uses a combination of lens types to achieve this.
Lens Type | Specifications | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
Aspheric (L1) | Diameter: 1.0 mm, f = 0.60 mm, NA = 0.83, n = 1.84 | Collimates excitation beams for efficient dye activation |
Achromatic Doublet (L2) | Diameter: 1.0 mm, f = 1.5 mm, NA = 0.33, n = 1.62/1.84 | Minimizes chromatic aberrations for sharper images |
Concave (L3) | Diameter: 1.0 mm, f = -4 mm, n = 1.48 | Increases scan angles for better fluorescence collection |
L4-L6 | Thorlabs #F950FC-A, #F240FC-780 | Collimate and focus fluorescence from multi-mode fibers |
Dichroic Mirrors | DM1, DM2, DM3 | Directs fluorescence into channels for multiplexed imaging |
Long-pass Filters | LPF1, LPF2, LPF3 | Filters wavelengths for improved detection accuracy |
You use these lenses to maximize the signal-to-noise ratio and signal-to-background ratio. High SNR and SBR help you detect even faint fluorescent signals, which is critical in fluorescence endoscopy. You often see molecular probes with fluorescent dyes that absorb photons and emit light at longer wavelengths. This process creates a clear fluorescent signal for you to observe.
Tip: Modulight’s laser technology can tailor the excitation light for your endoscope, making fluorescence endoscopy more precise.
You improve the performance of fluorescence endoscopy by using coated lenses. Advanced antireflective coatings, such as eBAND, use nanostructured layers with ultra-low refractive indices. These coatings reduce flare and ghosting, giving you sharp images even in low-light conditions. You also benefit from coatings that extend the bandwidth and manage angular dependency, which is important for NIR fluorescence imaging.
Recent advancements in coating and thin-filter optical technologies are resulting in more applications in the medical and life science industries, including optimizing NIR fluorescence endoscopic techniques. One such advancement, called the extended bandwidth and angular dependency (eBAND) lens coating, deploys a nanostructured layer with an ultra-low refractive index, which significantly enhances antireflection properties and reduces undesired flare and ghosting, thus delivering sharp, clear images even in very poor lighting conditions.
You use optical filters to control the angle of the laser beam and manage the full-width-at-half-maximum value. This control gives you clearer visibility of affected areas during fluorescence endoscopy. Optical filters also help you select the right wavelengths for NIR fluorescence imaging, which improves detection accuracy.
Optical filters enable precise control of the laser beam angle.
They help you manage the FWHM value for better clarity.
You achieve higher accuracy in NIR fluorescence imaging with the right filters.
You depend on these coated lenses and optical filters to enhance the quality of fluorescence endoscopy. They allow you to see subtle changes in tissue, which supports advanced diagnostic procedures and better patient outcomes.
You depend on advanced image transfer lenses to achieve outstanding optical clarity during endoscopic procedures. These lenses use innovative designs to move images from deep inside the body to your viewing device. Recent advancements, such as the metalens system, have transformed how you experience endoscope imaging. The metalens system allows you to use smaller endoscopes without losing clarity. You can now reach areas that were once impossible to visualize, like blood clots in the brain or diseased arteries.
Feature | Description |
|---|---|
Metalens System | Enhances image transfer, enabling smaller endoscopes and improved optical clarity |
Depth Sensing | Lets you access hard-to-reach areas with greater clarity |
Resolution | Delivers higher resolution for better diagnosis and optical clarity |
Size Reduction | Reduces endoscope diameter by over 50%, improving access and clarity |
Real-time Visual Feedback | Gives you immediate feedback, increasing efficiency and clarity |
Chromatic Aberration | Reduces color distortion, supporting better optical clarity |
Aperture Width | Features a 0.5 mm aperture, maximizing clarity in tight spaces |
Applications | Expands your ability to visualize complex medical conditions with clarity |
You gain real-time visual feedback, which helps you make quick decisions and reduces the risk of errors. The improved depth sensing and reduced chromatic aberration mean you see every detail with exceptional clarity.
Precision lenses take optical clarity to the next level. You use these lenses to enhance both the resolution and contrast of images during endoscopic procedures. High-definition endoscopes now offer up to a million pixels, giving you unmatched clarity. You can magnify mucosal images by up to 35 times, and optical zoom can reach 150 times magnification. This level of detail helps you spot even the smallest lesions.
Advanced lens designs improve light transmission, boosting optical clarity.
Better contrast lets you identify tiny abnormalities with greater clarity.
Multiple imaging modes support a wide range of diagnostic needs.
Note: 3D imaging with precision lenses increases your confidence in recognizing tumor boundaries and improves the accuracy of diagnosis.
Modern endoscope processors convert light into high-definition images with minimal artifacts. You benefit from clear, sharp visuals that support accurate and efficient endoscopic procedures. Precision lenses ensure you never miss important details, making every procedure safer and more effective.
You need to choose the right endoscope lens for clear images and reliable performance. Different lens types, such as objective, relay, rod, GRIN, cylindrical, and aspheric, each play a role in image formation and transmission. Materials like glass, fused quartz, and specialty coatings improve durability and clarity.
Glass lenses provide excellent light transmission and durability.
Plastic lenses offer lightweight options but may lower optical quality.
Autofocus systems and aspheric lenses help you achieve sharper images during endoscopy.
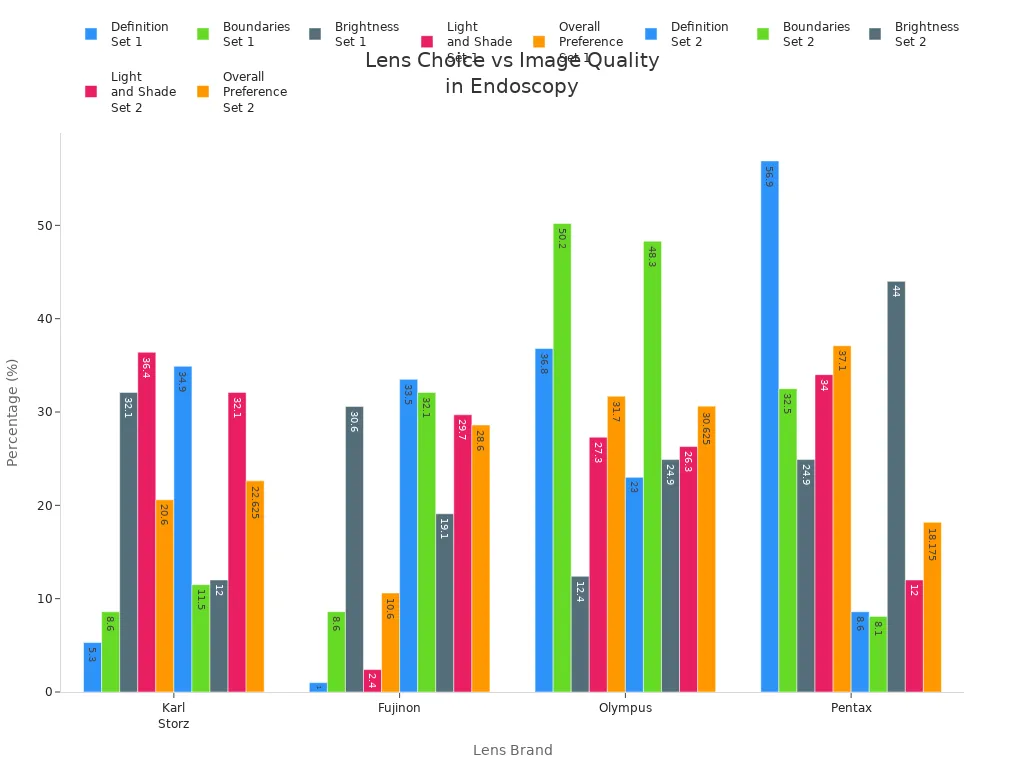
You should consider lens type and material when selecting an endoscope for Medical procedures. High-quality lenses reduce distortion and enhance clarity, which supports accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
You should rinse endoscope lenses with sterile water to remove debris. Use a soft brush to clean the lens surface. Always follow the manufacturer's cleaning instructions before sterilization. This step helps you prevent scratches and ensures effective sterilization.
Sterilization removes harmful microbes from endoscope lenses. You maintain image clarity and lens function by using proper sterilization methods. High temperatures or harsh chemicals can damage lenses, so always choose sterilization techniques recommended for your specific endoscope lenses.
Yes, you can reuse endoscope lenses after sterilization. You must inspect the lenses for damage or residue after each sterilization cycle. Proper sterilization ensures patient safety and maintains the quality of your endoscope lenses.
You can use steam sterilization, ethylene oxide gas, or low-temperature plasma for endoscope lenses. Each method has advantages. Steam sterilization is fast, while gas and plasma work well for heat-sensitive lenses. Always check your endoscope lenses' compatibility with the chosen sterilization method.
Sterilization protects patients from infection during Medical procedures. You eliminate bacteria, viruses, and fungi from endoscope lenses. Consistent sterilization keeps your Medical equipment safe and reliable for every procedure.
